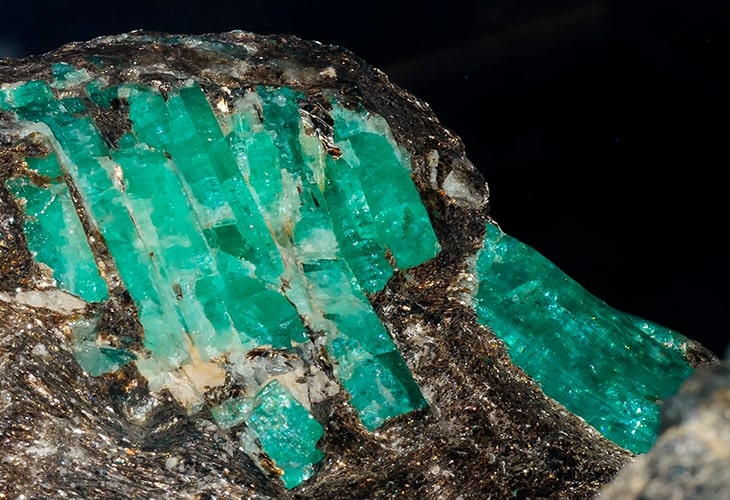
Emerald is actually a variation of green beryl, the colour of which is produced by an excess of chromium.
Like emerald, aquamarine, heliodorus and morganite are a variation of beryl (mineral species) with the formula Be3Al2(Si6O18). Hardness of 7.5 – 8 Mohs.
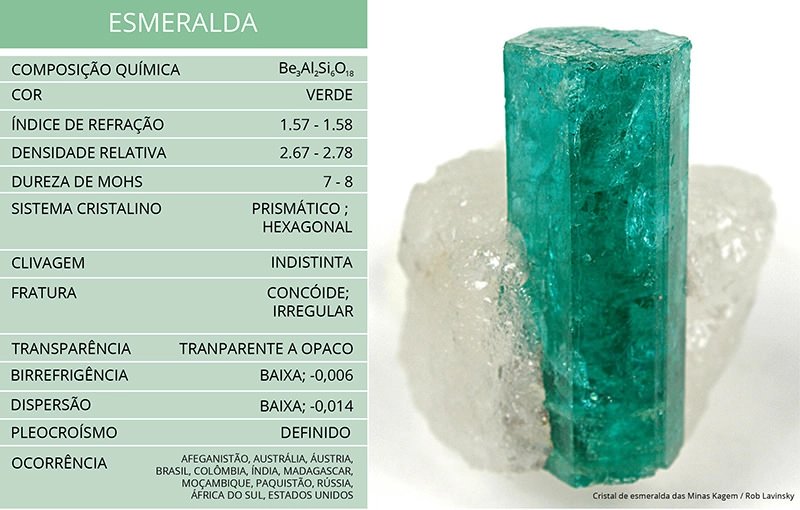
Emerald crystallises in the hexagonal system and its green hue varies from medium to dark green, depending on the percentage of chromium oxide (0.1 – 0.3%). A gemstone containing less than 0.1% chromium oxide is considered to be green beryl and not emerald.

Emeralds are found in many parts of the world, with each region providing emeralds with their own unique characteristics.
Their economic value is also indicated, with Colombian emeralds having the highest value.
The first emerald mines appeared in Egypt, but there is no longer any production in that country. It was traded in Babylon two thousand years before Christ, but was rare until the Renaissance, when South American deposits were discovered.

Pedra Esmeralda - Caracteristicas, Variedades e Qualidade
Today, emeralds are mined mainly in Colombia, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Tanzania, Madagascar and Brazil (Goiás, Bahia and Minas Gerais).
The emerald is considered one of the 4 most precious stones in the world, along with the ruby, the diamond and the sapphire. It is a very valuable stone and one of the oldest ever found.
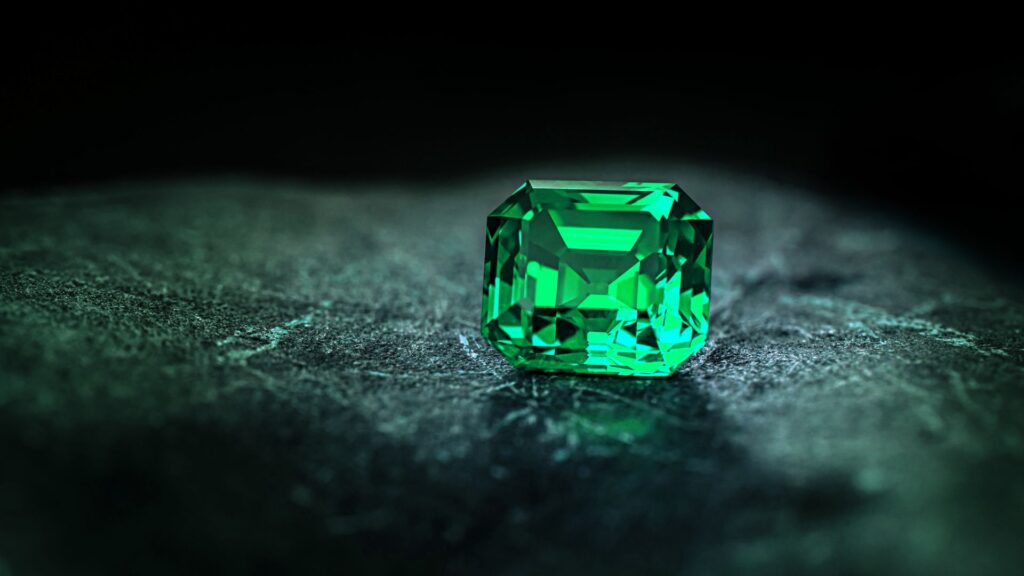
Emeralds are rarer and, depending on their quality, more expensive than diamonds. But they are the rarest of all gems, which is why they are often worth more than diamonds.
The best quality emeralds of 5 to 8 carats can be worth up to US$5,600 per carat. Gems of the same weight of average quality range from US$100 to US$580 per carat.
Emeralds have been commercially synthesised since the 1940s. Unlike other minerals, all production of synthetic stones is for jewellery.
Emerald can be confused with synthetic emerald, chromium diopside, chromolite, paraiba tourmaline, tsavorite, demantoid, uvarovite, composite gemstones, glass, plastic-coated beryl and diopside.
See Identifying a gemstone or precious stone is a difficult task.
Emerald names used in the market
- Colombian – the market name for high quality emeralds.
- Russian or Siberian – a less bluish name with more inclusions and a lighter colour than Colombian gems.
- Brazilian – a term sometimes used for light green coloured gemstones.
- Sandawana – a term used for deep green coloured gemstones, usually small in size and with many inclusions.
- Zambian – term used for slightly greyish gems.
Possible Emerald Treatments
- Filling of fractures or surface cavities with a hardening substance (good stability).
- Impregnation – with oils, waxes, resins or colourless plastics, not cured, in cracks or cavities to improve appearance (medium to good stability).
- Tinting – with coloured dye or oil (detection: dye concentrates in cracks).
- It is possible to eliminate traces of yellow, if they are due to additional iron content, by heat treatment at temperatures between 400 and 450°C.
Emerald quality factors
The gemstone has many special qualities, but experts agree that the most important is the colour.

Mainly for the green pattern. And knowing how to differentiate between emerald values requires a well-trained eye to spot the sometimes subtle variations that make it worth more.
There are four factors that determine the quality of an emerald:
1. Colour
From light to very dark green to a very strong bluish green.
The most desirable colours are bluish-green to pure green, well coloured but not dark, as the most appreciated are the transparent ones.
Its colour is uniform and intense, unmatched by anything else in nature.
And if it has a very yellowish or bluish hue, the stone is a different variety of beryl and its value will drop accordingly.
Chromium, vanadium and iron are the trace elements that give emerald its colour. The presence or absence of each and their relative amounts determine the exact colour of an emerald crystal.
2. Clarity
From transparent to translucent.
Emeralds contain inclusions that are visible to the eye without the use of special equipment, which is why some dealers and consumers understand and accept the presence of inclusions. Clean emeralds are more valuable because they are rarer.
However, if inclusions affect the transparency and clarity of the stone, this will have a negative effect on the trade and drastically reduce its value.
3. Cutting
The cutter must consider the depth of colour, durability and inclusions of the rough when cutting. And mistakes in cutting can result in weight loss, reducing the value of the gem.
Emeralds already have significant natural fractures, so the cutter must design the cut to minimise the effect of these fractures on the stone. Another important factor is that emeralds are very fragile, making them susceptible to damage during the procedure or through careless daily use.
Care should also be taken with the type of cut that is made, as this can change the tone and saturation of the stone, leaving a darker pale stone with a deep cut, or even a less facetted stone with a shallow cut.
4. Km
Quality for quality, the price of an emerald can rise dramatically as it increases in size. Therefore, in jewellery shops, prices will vary greatly depending on the carat of the emerald.
Publicações Relacionadas
The malachite stone is a distinctive gemstone - Features
Characteristics of the Paraíba Tourmaline, a rare gemstone
Tiger Eye Stone - Characteristics and Cutting
Quartz Stone - Characteristics, Colours and Varieties
Aquamarine Stone is used in the jewellery industry - characteristics
Agate Stone - Characteristics, Types, Colour and Cutting
Amethyst stone - characteristics, marketing and valuation
Jewellery made from different types of coral - Features
Opala é uma das mais belas pedras preciosas encontradas no Brasil
Diamonds have 4 basic classifications, weight, colour, purity and cut
Characteristics of Topaz and Imperial Topaz gemstones
Identifying a gem is a difficult task
Sapphire is the purity of nature and a symbol of honesty
Ruby Stone - Characteristics, Colours and Cutting
Jade stone - characteristics, colour, classification and cutting
Pindobaçu (BA), known as the capital of emeralds
Tourmaline: Learn about its characteristics and varieties
This post is also on:
![]() Português
Português ![]() English
English ![]() Deutsch
Deutsch ![]() Español
Español ![]() Français
Français