Trindade and Martim Vaz – History, shipwrecks, geography, flora and fauna
Trindade and Martim Vaz Archipelago
Trindade e Martim Vaz is a Brazilian archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, a Federal Territory off the coast of Espírito Santo, about 1,200 kilometres east of Vitória.
It consists of two main islands (Trindade and Martim Vaz), separated by 48 kilometres, with a total area of 10.4 km².
Trindade and Martim Vaz are considered by navigators to be an immense wall in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean and are uninhabited, except for a garrison of 32 Brazilian Navy personnel on Trindade Island.

Discovery and history
During the reign of King Manuel I of Portugal, the island of Martim Vaz was discovered in 1501 by the Galician navigator João da Nova.
About a year later, the Portuguese navigator Estêvão da Gama visited the largest island and named it “Ilha da Trindade”.
The islands remained under Portuguese rule until Brazil’s independence, when they became Brazilian.
In 1890 the United Kingdom occupied Trindade, but the British abandoned the islands in 1896 after an agreement between the two countries, mediated by Portugal.

Videos about “Trindade Archipelago


Ilha de Trindade e Martim Vaz - Expedição20:36

Vegetação na Ilha de Trindade03:13

Samambaias na Ilha de Trindade07:39

Animais na Ilha de Trindade03:13

Ilha de Trindade - Episódio 106:18

Ilha de Trindade - Episódio 206:08

Ilha de Trindade - Episódio 304:56

Ilha de Trindade - Episódio 407:04

Ilha de Trindade e Martim Vaz - Reportagem23:11
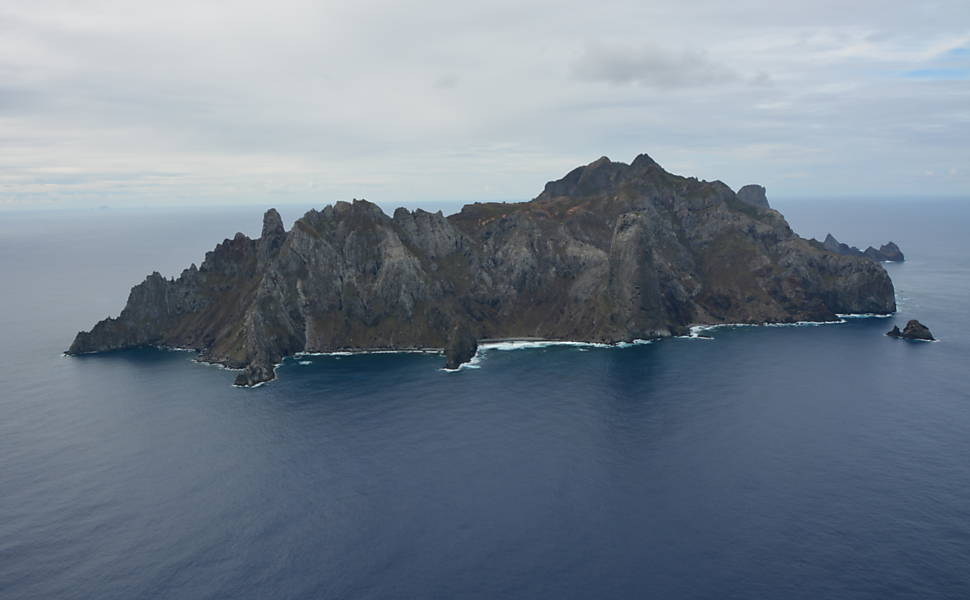
Martim Vaz Islands
Martim Vaz is a group of islands that includes the main island, Martim Vaz (with a maximum altitude of 175 metres), two steep and inaccessible islets ( Ilha do Norte, with a maximum altitude of 65 metres, and Ilha do Sul, with a maximum altitude of 122 metres), and several smaller rocks, such as Rocedo Agulha.
The Martim Vaz complex covers a total area of 0.3 square kilometres (30 hectares).
The vegetation is mainly undergrowth, with the presence of rare bushes at the top, which are strongly whipped by the wind. The fauna consists only of crabs, endemic spiders and hundreds of migratory birds.
The only less risky way to disembark is by helicopter, due to the vertical and flat topography at the top of the island.

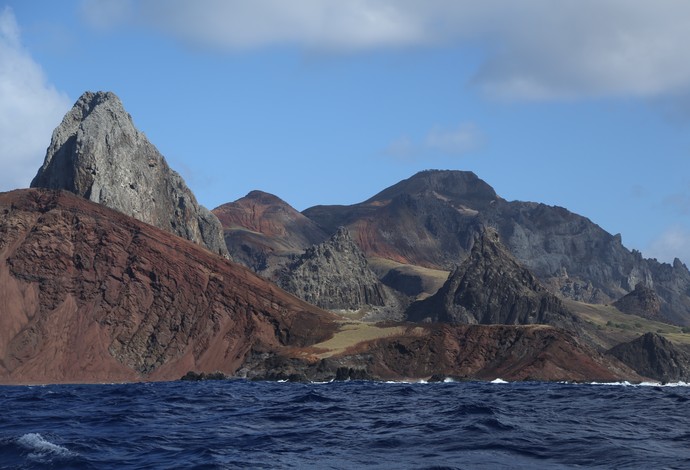
Trindade Island
Trindade is a volcanic island off the coast of the state of Espírito Santo, Brazil, which forms an archipelago with Martim Vaz. With an area of 9.2 square kilometres, it is located 1,167 kilometres from the mainland.

Discovered in 1512 by João da Nova, the island was visited in 1514 by Juan de la Cosa, who named it Santa Maria Esmeralda.
In 1768 the Frenchman La Pérouse tried to climb the rocks, but two of his sailors died in the attempt. In their honour, the name of the archipelago was changed to Martim Vaz.
In 1951, the Brazilian Navy wanted to formally take possession of the islands, and a military garrison attempted to raise the flag on the main island, but the ship sank, resulting in the deaths of 12 sailors.
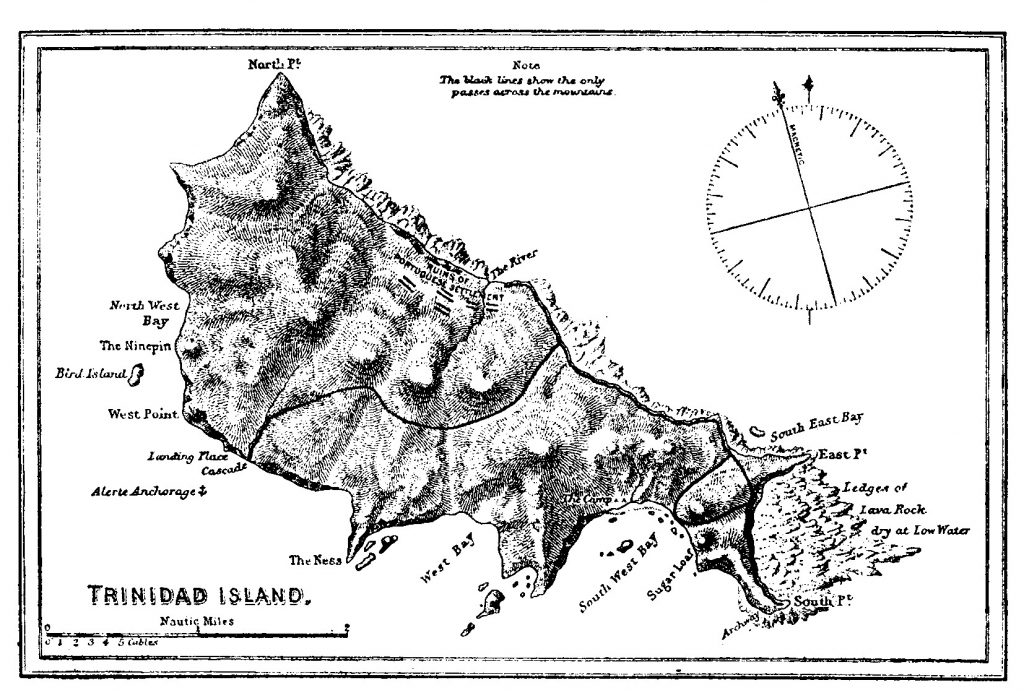
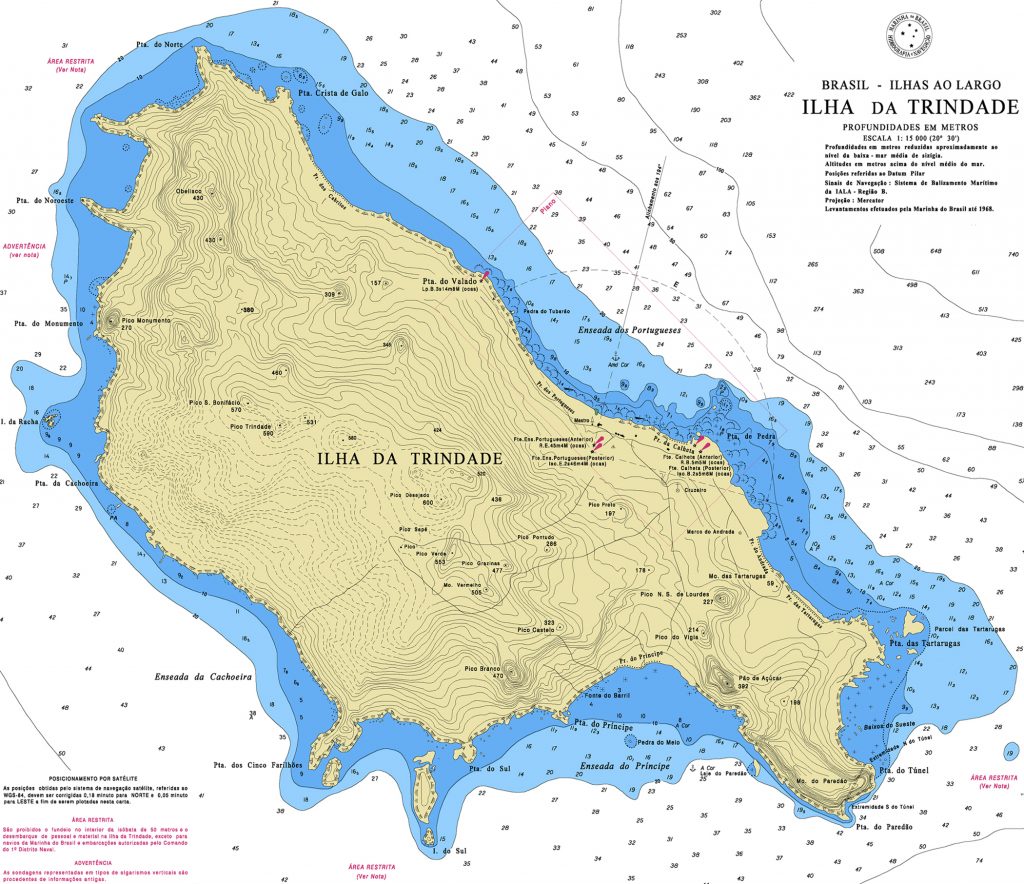
Geography of the islands
The islands of Trindade and Martim Vaz are located 1,200 km off the coast of Vitória, in the centre of the South Atlantic.
The archipelago consists of two main islands (Trindade and Martim Vaz), two steep and inaccessible islets (Ilha do Norte and Ilha do Sul) and several smaller rocks, such as Agulha Rock.
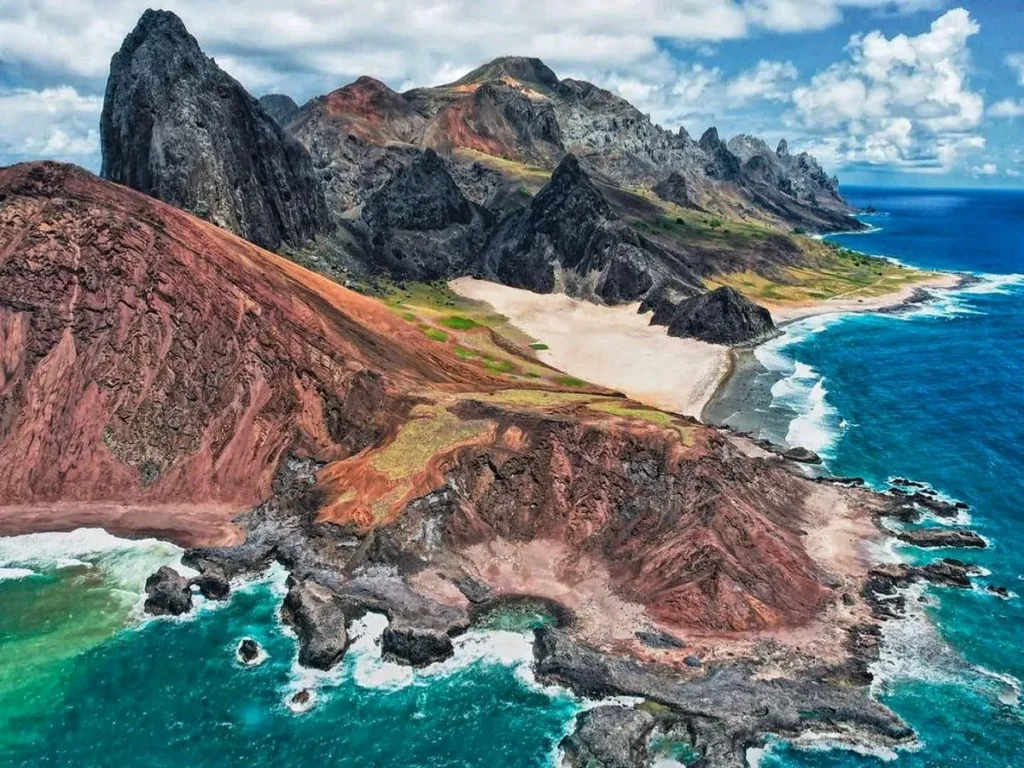

Island Geology
The island of Trindade has several volcanic centres, with the most recent volcanic activity recorded about 50,000 years ago at the Paredão Volcano.
This volcano produced a pyroclastic flow that formed an ash cone.


Flora and fauna of the islands
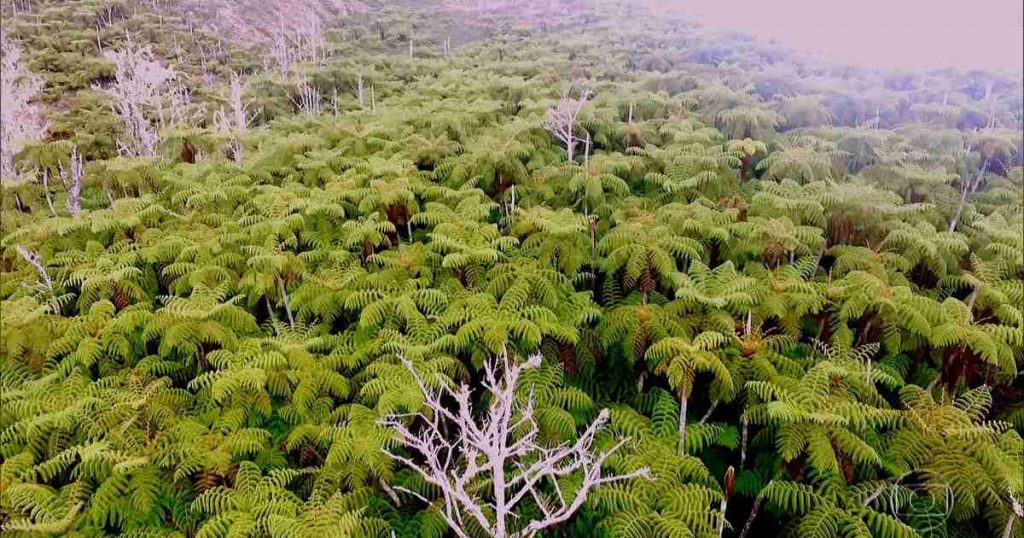
The ecosystem of the islands of Trindade and Martim Vaz is the subject of research by the National Museum. A study by the naturalist Ruy Alves identified 124 botanical species, 11 of which are endemic.
The most important plant species is the giant fern, while the yellow crab (Geocarcinus lagostoma, Grapsus grapsus) is the most important terrestrial species, found at high altitudes.

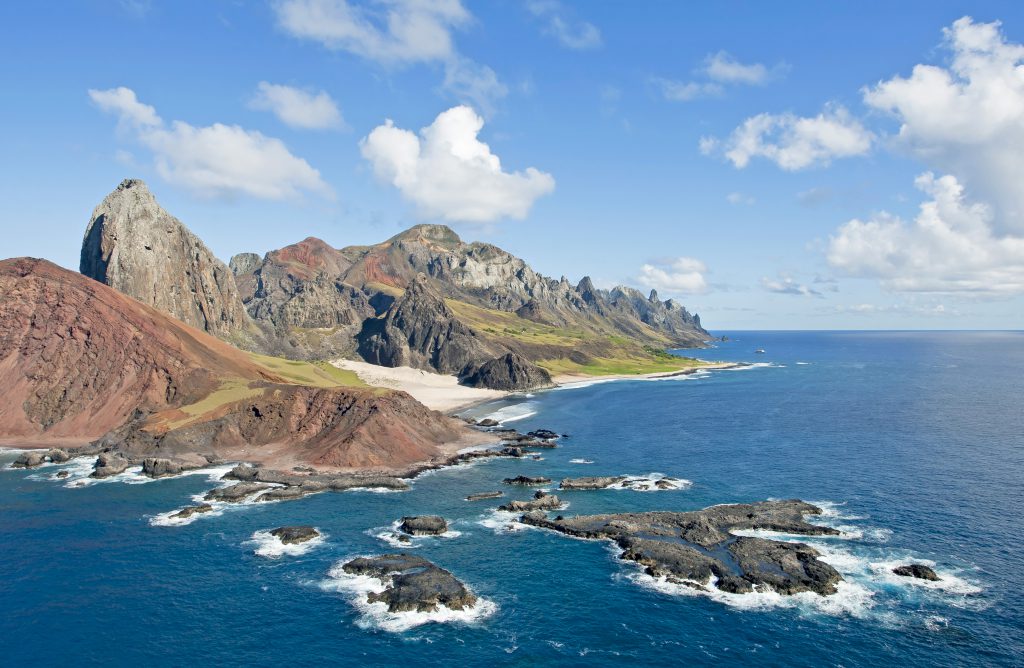
The region is also a habitat for seabirds, and the surrounding waters are home to a wide variety of marine species, including the green turtle (Chelonia mydas) and the hawksbill turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata).
Beaches of the Archipelago

The beaches of the Trindade and Martim Vaz Archipelago include
- Cabritos Beach
- Portuguese beach
- Calheta beach
- Andradas Beach
- Turtle Beach
- Parcel Beach
- Tunnel Beach
- Ponta do Túnel Beach
- Príncipe Beach
- Rubbish Beach
- Farilhões
- Eme Beach
- Cachoeira Beach
- Northwest beach
- Orelhas Beach
- North Point
Economic exploitation
The military presence on Trindade is considered strategic. In 1957, the Brazilian government delegated the task of guarding and occupying the island to the navy, in accordance with international agreements on the economic exploitation of maritime zones.

Shipwrecks
The sea in Trindade is notoriously dangerous, with shipwrecks dotting the landscape of The Portuguese Beach. One emblematic shipwreck involved the Chinese fishing vessel Hwa Shing, whose crew mutinied and were arrested by the Brazilian navy.
Conclusion
The islands of Trindade and Martim Vaz are of great ecological, historical and economic importance to Brazil. The archipelago is home to a rich biodiversity and represents a strategic point for the exploitation of resources in the South Atlantic.
Publicações Relacionadas
Surfing in Fernando de Noronha: Everything You Need to Know
Anchieta Island: History, Beaches, and Nature
Atol das Rocas - Origin, Biology, Climate and Shipwrecks
Diving in the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago
History of Itaparica Island in the Baía de Todos os Santos
The Marajó Archipelago
Brazil has oceanic and continental islands
Jararaca-ilhoa: Endemic Species of Queimada Grande
Ilhabela is the hottest spot on the north coast of São Paulo State
Itamaracá Island: Your Ultimate Guide to Tropical Bliss in Brazil
Fernando de Noronha archipelago
Fernando de Noronha Beaches: A Complete Guide
How to get there, when to go and what to do in Fernando de Noronha?
The island of Santa Catarina is part of the municipality of Florianópolis
São Pedro and São Paulo Archipelago
Spinner Dolphins in Fernando de Noronha: A Guide
Ponta do Boi Lighthouse in Ilhabela
Experience the Tropical Paradise of Ilha Grande in Rio de Janeiro
This post is also on:
![]() Português
Português ![]() English
English ![]() Deutsch
Deutsch ![]() Español
Español ![]() Français
Français