Spinner dolphins in Fernando de Noronha: a natural spectacle In the bay of Baía dos Golfinhos, in Fernando de Noronha, there is a high concentration of spinner dolphins (Stenella longirostris), an oceanic and tropical species known for its acrobatic behaviour, jumping out of the water with up to seven turns […]
Fernando de Noronha Archipelago
Fernando de Noronha Archipelago: Geography and Tourist Attractions
The Fernando de Noronha Archipelago is one of Brazil’s most important natural heritage sites, recognised both for its biodiversity and its potential for sustainable tourism.
Located in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean, it is part of the state of Pernambuco and is a protected area and World Heritage Site, declared by UNESCO in 2001.
Fernando de Noronha is an example of sustainable tourism in Brazil, with controlled access and strict environmental policies.
1. Geographical location and physical aspects
Fernando de Noronha is located about 545 kilometres from the capital of Pernambuco, Recife, and about 350 kilometres from the coast of Rio Grande do Norte.
The archipelago is of volcanic origin and is made up of 21 islands, islets and rocks, with a total area of about 26 km², of which 17 km² correspond to the main island, which is the only one inhabited.
The highest point is Morro do Pico, with an altitude of 321 metres.
The main island is home to Vila dos Remédios, the urban centre where the administrative, historical and commercial functions of the city are concentrated.
2. Climate and vegetation
Fernando de Noronha has a tropical climate with two well-defined seasons: a rainy one (from March to July) and a dry one (from August to February).
The average annual temperature is about 26°C.
The vegetation consists mainly of species adapted to the semi-arid and coastal climate, including grasses, shrubs and areas of dry forest.
3. Environmental aspects and conservation
Most of the archipelago is protected by two nature reserves:
- Fernando de Noronha Environmental Protection Area (APA) – covers urbanised areas and allows sustainable economic activities.
- Fernando de Noronha National Marine Park – managed by ICMBio, restricts access to areas of integral conservation.
Since 2001, the archipelago has been recognised by UNESCO as a World Natural Heritage Site, together with Atol das Rocas.
4. Tourist Attractions
4.1 Beaches
- Baía do Sancho: voted the most beautiful beach in the world several times, it has controlled access and is part of the National Marine Park.
- Baía dos Porcos: Famous for its natural pools between volcanic rocks, with views of the “Two Brothers”.
- Praia do Leão: One of the wildest of the island, it is a nesting place for sea turtles.
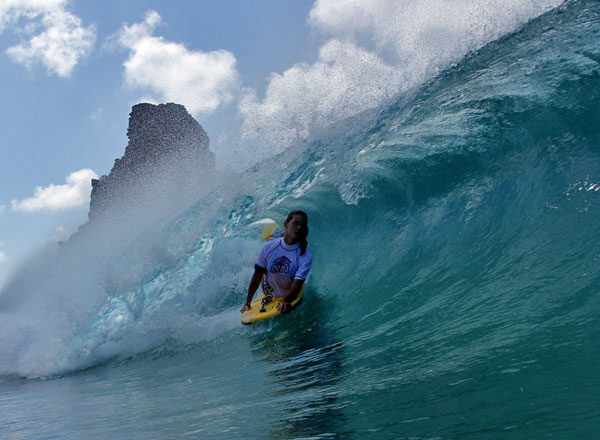
- Cacimba do Padre: popular with surfers for its quality waves.
4.2 Trails and ecotourism
Fernando de Noronha’s trails are regulated and some require reservations:
- Atalaia Trail: leads to a natural pool rich in biodiversity.
- Capim-Açu Trail: longer and more challenging, offering unique views and landscapes.
- Abreus and Pontinha-Caieira Trails: pass through areas of great environmental sensitivity.
4.3 Diving and marine life
The island is one of Brazil’s most important diving destinations, offering
- Scuba diving: at sites such as Pedras Secas and Naufrágio do Porto.
- Snorkelling: In Sueste, Porcos and Sancho bays.
- Dolphin watching: especially in Dolphin Bay.
Projects such as the Tamar Project and the Spinner Dolphin Project work to conserve marine life.
5. Infrastructure and access
5.1 Transportation
Access to the archipelago is by air, with regular flights from Recife and Natal. Internally, tourists use buggies, vans, taxis or footpaths.
5.2 Accommodation and food
Accommodation ranges from cosy inns to sophisticated resorts. The local cuisine favours seafood and regional ingredients, with renowned restaurants such as Zé Maria and Varanda.
6. Environmental legislation and fees
- Environment Conservation Fee (TPA): Compulsory and charged per day of stay.
- National Marine Park Entrance Fee: required to access trails and beaches within the park.
Both fees can be paid in advance through the official websites of the Pernambuco government and ICMBio.
Wreck of the Corvette Ipiranga in Fernando de Noronha
Corvette Ipiranga (V-17): One of Brazil’s most iconic shipwrecks One of Brazil’s most famous shipwrecks, the Brazilian Navy’s Corvette V-17 – Ipiranga, lies at a depth of around 62 metres in the waters off Ponta da Sapata in the Fernando de Noronha archipelago. Very well preserved by the island’s dive […]
Fernando de Noronha Beaches: A Complete Guide
Fernando de Noronha Beaches: A complete guide Fernando de Noronha is an archipelago of stunning beaches, each with its own unique characteristics. Some are ideal for snorkelling, others for swimming, observation, surfing and other activities. Video about the beaches and attractions of Fernando de Noronha See the map of beaches […]
Fernando de Noronha archipelago
Fernando de Noronha Archipelago: History, Geography and Tourism The Fernando de Noronha Archipelago consists of 21 islands, islets and rocks of volcanic origin in the South Equatorial Atlantic Ocean. The main island, also known as Fernando de Noronha, is the only inhabited island and accounts for about 91 per cent […]
Surfing in Fernando de Noronha: Everything You Need to Know
Surfing in Fernando de Noronha: The Brazilian Hawaii of swells Fernando de Noronha is widely regarded as one of the best surfing destinations in Brazil and is often referred to as the Brazilian Hawaii due to its powerful and consistent swells. Wave Season The surfing season in Fernando de Noronha […]
Diving in the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago
Diving in the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago Diving is Fernando de Noronha’s biggest attraction. The waters are so transparent that the visibility on the seabed can exceed 40 metres. It is an excellent place to observe a natural system with around 230 species of fish, fifteen species of coral and […]
How to get there, when to go and what to do in Fernando de Noronha?
Fernando de Noronha: When to go and what to do Fernando de Noronha is located 545 kilometres from Recife, capital of the state of Pernambuco; 360 kilometres from Natal, capital of the state of Rio Grande do Norte; and 710 kilometres from Fortaleza, capital of the state of Ceará. How […]